Urine is more than just a waste product—it’s a powerful indicator of your overall health. From hydration levels to kidney and liver function, your urine’s color, odor, and frequency can provide valuable insights into what’s going on inside your body. Understanding these signs can help you identify potential health concerns early and seek medical attention when necessary.
Let’s take a closer look at what your urine color and smell might be telling you about your liver, kidneys, and overall health.
What Does Urine Color Indicate About Your Health?
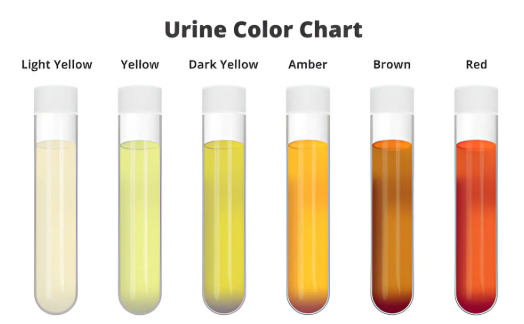
Healthy urine typically ranges from pale yellow to light amber due to a pigment called urochrome. This color variation is influenced by hydration levels and diet. However, changes in urine color can sometimes signal underlying health issues.
Common Urine Colors and Their Meanings
Clear or Very Light Yellow Urine
- Indicates overhydration or excessive fluid intake.
- Can result from diuretic use (medications that increase urine production).
- While generally not dangerous, persistently clear urine may dilute essential minerals.
Dark Yellow or Honey-Colored Urine
- Suggests dehydration due to low fluid intake.
- May indicate excessive sweating or heat exposure.
- Drinking more water usually restores a normal urine color.
Orange Urine
- Often caused by high doses of vitamin B2 or medications like phenazopyridine (used for UTIs).
- Dehydration can also lead to orange-colored urine.
- In some cases, liver or bile duct issues can turn urine orange, especially if accompanied by light-colored stools and yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice).
Pink or Red Urine
- Can be caused by certain foods, such as beets, berries, and rhubarb.
- Some medications (like rifampin and phenazopyridine) may cause reddish urine.
- Blood in the urine (hematuria) can indicate:
- Kidney disease
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Prostate problems in men
- Bladder or kidney tumors (seek medical evaluation if unexplained).
Blue or Green Urine
- Often results from food dyes or artificial coloring in processed foods.
- Certain medications, including propofol (anesthetic) and promethazine (allergy medication), can turn urine blue or green.
- In rare cases, blue or green urine can indicate a bacterial infection or genetic disorder.
Dark Brown or Cola-Colored Urine
- May be a sign of severe dehydration or liver disease.
- Could indicate rhabdomyolysis, a condition where muscle tissue breaks down rapidly.
- If urine remains dark despite adequate hydration, it may be due to bile pigments from liver dysfunction.
Foamy or Cloudy Urine
- Occasional foamy urine is normal, but persistent foaming may signal excess protein, which could be an early sign of kidney disease.
- Cloudy urine can result from:
- UTIs
- Kidney infections
- Dehydration
- Excess minerals or phosphates in the diet
Does the Smell of Urine Indicate a Health Condition?
Urine typically has a mild odor, but changes in smell can indicate dietary factors or health issues.
Common Urine Odors and Their Causes
Strong Ammonia-Like Odor
- May result from dehydration, making urine more concentrated.
- Can be caused by eating sulfur-rich foods like asparagus, onions, or garlic.
- Infections, such as UTIs, can also contribute to a strong smell.
Sweet or Fruity Smell
- Could indicate diabetes or uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
- Results from ketones in the urine, a byproduct of fat breakdown when glucose isn’t available for energy.
Foul or Fishy Odor
- Often linked to urinary tract infections (UTIs) or bladder infections.
- May also suggest trimethylaminuria, a rare metabolic disorder that causes a fishy body odor.
Maple Syrup-Like Smell
- Could be a sign of maple syrup urine disease (MSUD), a rare genetic disorder that affects amino acid metabolism.
If urine odor changes suddenly and is accompanied by pain, fever, or other unusual symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention.
How Often Should You Urinate Each Day?

The average person urinates six to eight times a day, but frequency can vary based on:
- Fluid intake
- Caffeine or alcohol consumption (which increase urination)
- Medication use (such as diuretics)
- Pregnancy or aging
Frequent urination could be a sign of:
- Urinary tract infections
- Diabetes
- Overactive bladder syndrome
- Enlarged prostate in men
- Interstitial cystitis in women
If frequent urination is persistent, painful, or accompanied by discomfort, consult a doctor for further evaluation.
Is It Normal for Urine to Contain Sediment?

Urine sediment refers to particles visible in urine, which can be caused by diet, infections, or kidney-related issues.
Common Causes of Urine Sediment
1. Diet and Supplements
- Excess vitamin D, phosphorus, or calcium may cause visible particles in urine.
- Certain foods, such as dairy or high-mineral content foods, can contribute to sediment.
2. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Bacterial infections in the bladder or kidneys can cause urine to appear cloudy or contain pus or blood traces.
- Symptoms often include burning sensation, frequent urination, and strong odor.
3. Kidney Infections
- Often develop from untreated UTIs and may cause:
- Fatigue, chills, fever, and nausea
- Lower back pain
- Visible sediment in urine
4. Chyluria (Chylous Urine)
- A condition where lymphatic fluid leaks into the kidneys, leading to milky or fatty urine.
- Characterized by a whitish, oily layer settling in the urine.
5. Medications
- Certain drugs, including vitamin B and C supplements, diabetes medications, and phosphorus-rich drugs, can increase urine sediment.
If urine contains persistent sediment or is accompanied by discomfort, seek medical advice for a proper diagnosis.

Conclusion: Pay Attention to Your Urine for Better Health
Your urine can tell you a lot about your health. By paying attention to color, smell, and frequency, you can detect potential health issues early. While some urine changes are harmless and diet-related, persistent abnormalities could signal kidney problems, liver disease, diabetes, or infections.
If you notice unusual urine color, persistent odor, or frequent discomfort, consult a healthcare professional to rule out serious conditions. Taking care of your urinary health is a simple yet essential step toward overall well-being.


