Ever wonder what the color of an egg yolk reveals? You crack open an egg, and there it is—a vibrant yellow, or maybe even a pale hue. But did you know that the color of an egg yolk can tell you a lot about where that egg came from? This small detail is often overlooked, yet it reveals key insights into the diet and health of the hen that laid it. Let’s crack open the facts and find out how to choose the healthiest eggs.
Why Yolk Color Matters: The Nutrient Connection
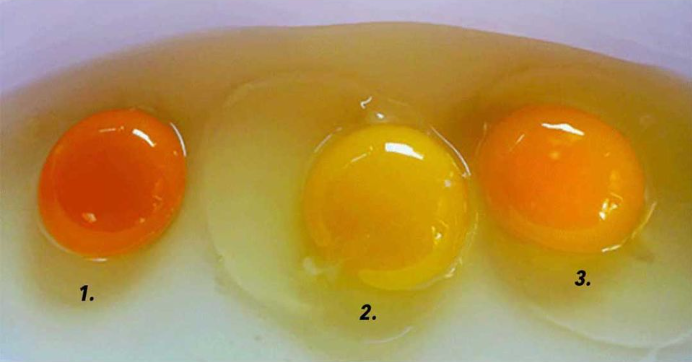
When it comes to egg yolks, color is more than just a visual feature; it’s a direct indicator of the hen’s diet and, ultimately, the nutritional value you’re getting. The nutrient content of an egg yolk reflects what the chicken was fed, and this affects not only the richness of the color but also the amount of essential vitamins and minerals packed into each egg.
Darker yolks generally signify a more nutritious egg. Hens that eat a varied, nutrient-rich diet produce darker yolks, which contain higher levels of beneficial nutrients like vitamins A and E, as well as omega-3 fatty acids. Lighter yolks, on the other hand, often indicate a more restricted diet and a lower nutrient profile.
The Types of Eggs and What Their Yolk Color Tells Us
To better understand what you’re eating, let’s explore the three main types of eggs you’ll encounter: pastured eggs, free-range eggs, and caged eggs. Each type varies not only in yolk color but also in nutritional content.
1. Pastured Eggs: The Gold Standard for Nutrition
Pastured eggs are laid by chickens that roam freely outdoors and consume a varied diet that includes not only grains but also insects, plants, and seeds. This diverse diet results in vibrant, darker yolks that are rich in nutrients. Pastured eggs contain higher levels of vitamin A, vitamin E, and omega-3 fatty acids, making them the most nutritious option available.
Hens raised in pastured environments also lead healthier, less stressful lives, which further contributes to the quality of their eggs. If you notice a deep orange or dark yellow yolk, you’re likely looking at a pastured egg.
Key Nutrients in Pastured Eggs:
- Vitamin A: Boosts immune function and improves eye health.
- Vitamin E: Acts as a powerful antioxidant, helping to prevent cell damage.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Promote heart health by lowering cholesterol and blood pressure.
Pastured eggs are often more expensive, but they offer a nutritional boost that’s well worth the cost.
2. Free-Range Eggs: A Solid, Middle-Ground Option
Free-range eggs come from hens that have access to the outdoors, though their diets are typically less diverse than those of pastured hens. Free-range chickens usually eat a grain-based diet supplemented with insects and plants they find in their environment. This access to a somewhat varied diet produces yolks that are more vibrant than those from caged hens but generally lighter than pastured egg yolks.
Free-range eggs contain more nutrients than caged eggs, especially in terms of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins. While they might not be as nutrient-dense as pastured eggs, they’re still a healthy choice, especially if you prioritize eggs from hens that are given some level of freedom to roam.
Benefits of Free-Range Eggs:
- Richer in omega-3s than caged eggs.
- Lower in saturated fat compared to factory-farmed eggs.
- Produced by chickens with better living conditions, which can positively impact egg quality.
3. Caged Eggs: The Least Nutritious Choice

Caged eggs are laid by hens that spend their lives in confined cages, often with minimal movement and limited access to natural light. These chickens are typically fed a diet solely of grains, which lacks variety and nutrients. This restricted diet results in pale, light-yellow yolks that contain fewer vitamins and minerals.
Most supermarket eggs come from factory farms where hens are raised in cramped conditions and fed an industrial diet. While these eggs are the cheapest option, they also offer the least nutritional value. For those looking to maximize the health benefits of their eggs, caged eggs are generally the least desirable option.
Downsides of Caged Eggs:
- Lower levels of omega-3 fatty acids.
- Less vitamin A and E compared to pastured or free-range eggs.
- Often contain higher amounts of saturated fats.
Free-Range vs. Factory Farmed Eggs: Nutritional Differences
So, why choose free-range or pastured eggs over factory-farmed options? The answer lies in the nutrients they offer. Free-range and pastured eggs contain more vitamin A for immune health, vitamin E for cell protection, and omega-3 fatty acids to support cardiovascular health. Additionally, these eggs often have lower levels of saturated fat and cholesterol, which makes them a healthier choice overall.
While free-range and pastured eggs tend to cost more, their nutritional benefits outweigh the extra expense. For those concerned with both health and ethical farming practices, choosing eggs with darker yolks is a wise decision that supports both wellness and animal welfare.
How to Identify the Healthiest Eggs
Next time you’re at the grocery store, pay close attention to the egg carton labels. Words like “pastured” and “free-range” indicate that the hens likely had access to a varied diet and open spaces. Caged eggs will typically lack these labels, and while they might be cheaper, they’re less nutrient-dense.
If you’re buying eggs directly from a local farm, ask about the hen’s diet and living conditions. Most small-scale farmers are happy to share this information, and knowing more about where your eggs come from can help you make an informed choice.
Checking Yolk Color
When you crack open an egg, examine the color of the yolk. Darker yolks are a good sign that the egg contains higher levels of beneficial nutrients. While pale yolks aren’t necessarily harmful, they indicate a more limited diet, which means you’re likely missing out on essential vitamins and healthy fats.
Why Yolk Color Isn’t Just About Nutrition
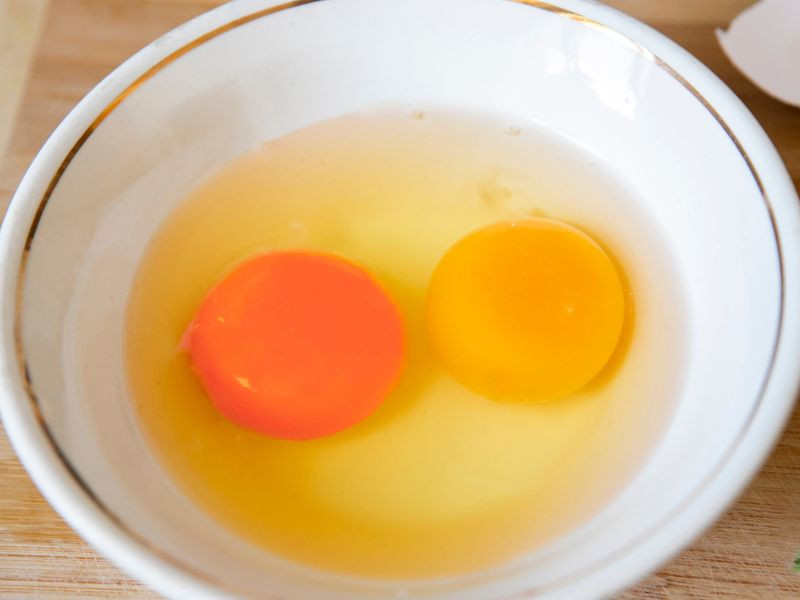

Beyond the health benefits, the color of the yolk can also reflect the ethical aspects of egg production. Eggs from pastured and free-range hens come from farms that allow the animals to live more naturally. By choosing eggs with darker yolks, you’re supporting farming practices that prioritize animal welfare, sustainability, and a higher quality of life for the hens.
Conclusion: The True Value of Darker Yolks
The next time you crack open an egg, take a closer look at the yolk. A darker hue signals a more nutritious and ethically sourced egg, one that’s packed with vitamins, healthy fats, and essential nutrients. While pastured and free-range eggs may cost a bit more, they offer a significant return on your investment in terms of health benefits.
So, is it worth paying extra for those rich, golden yolks? Absolutely. Not only are you nourishing your body with better nutrients, but you’re also supporting responsible farming practices. Share this information with friends and family to spread the word about the benefits of choosing darker, nutrient-rich eggs straight from the farm.


